Philip Grant continues his Guest series.
Welcome back to this story of an Indian solicitor who lived in Wembley around 90 years ago. If you missed Part 1, you can find it here.
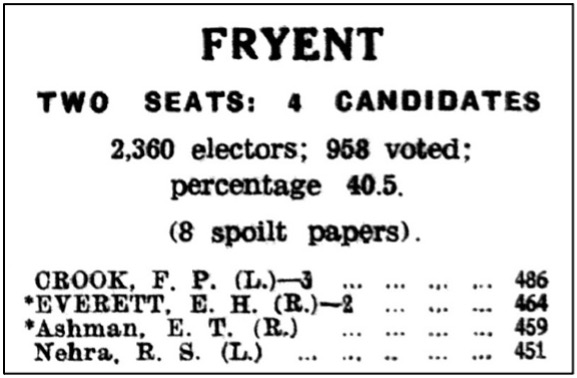
We left Ram Singh Nehra when he was standing as a Labour candidate for Fryent Ward, in elections for the new Wembley Council in March 1934. I asked: ‘would the people of Wembley in the 1930s vote for a man who wasn’t white?’ The answer was “yes”, but not quite enough of them to win him a seat on the Council. Whether his colour meant that he didn’t receive the small number of extra votes which would have seen him elected is something we will never know.
The Fryent Ward election result, from the “Wembley News”, 30 March 1934. (Brent Archives)
The Fryent Ward count, at Wembley Council’s Park Lane School on the evening of the election, must have been a tense affair. The result was very close, with only 35 votes separating Mr Crook, who topped the poll, from his fellow Labour candidate, Mr Nehra, at the foot of the list. In between were the two representatives of the Ratepayers’ Association, both existing Kingsbury councillors. Mr Ashman, who’d been Chairman of Kingsbury U.D.C., was so shocked to lose his seat that he demanded a recount!
The “Wembley News” report about Labour’s 1934
Fryent Ward election campaign.
(From the local newspaper microfilms at Brent Archives)
The newspaper report above shows how good canvassing in Fryent Ward beforehand had helped the Labour Party to win a local Council seat in Kingsbury for the very first time. This enabled them to ensure that all their likely supporters, who might not have been able to get to the polling station at Fryent School without assistance, were taken there by motor car to vote!
You might not expect that a “working class” party in 1934 could muster ‘a fleet of cars’ on polling day, but that is where Mr Nehra and his wide circle of friends played their part. Imagine the surprise of some residents, when a chauffeur driven limousine, with a coat of arms on its side, drew up outside their home to take them to the polling station! It had been loaned for the day by the Saudi Arabian Ambassador.
Sheikh Hafiz Wahba (and his limousine) in 1930. (Image from the internet)
Sheikh Hafiz Wahba was the Saudi Ambassador to the UK from 1930 until 1956. You may remember that he was one of the VIP guests at the Nehra’s Garden Party in July 1934, and he had come to know Ram Singh Nehra quite well. This was partly because Nehra’s Central Hindu Society saw Hinduism as a cultural identity much as a religion, and was keen on promoting Hindu-Muslim co-operation.
There is evidence of this from a 1935 report in “The Indian”, headed “Prophet’s Birthday”:
‘The Muslim Society in Great Britain held a reception on Wednesday, the 12th of June, at 8 p.m., at Portman Rooms, Baker Street, to celebrate the Birthday of the Holy Prophet Mohammad. His Excellency Sheikh Hafiz Wahba, the Saudi Arabian Minister to the Court of St. James’s, was in the chair.
Proceedings began with a recitation from the Qoran. Before starting further proceedings, the following message from Mr. R. S. Nehra, the President of the Hindu Society, was read — To the President, British Muslim Society, London:
Dear Sir,
Hearty congratulations on the celebration of the birthday of the Holy Prophet. His example is a beacon guidance to all human beings of the necessity, practicability and virtues of democracy in daily life.
Sorry my wife’s serious illness prevents me from joining you all this evening.’
Sir Abdul Qadir in 1935. (Image from the internet)
Sir Abdul Qadir was a leading member of The Muslim Society at the time, and like Nehra was also born in Ludhiana. Nehra’s good relations with the Muslim community may well date back to his childhood. Although Ludhiana was in the
Punjab, when Nehra was growing up there in the early 20th century only around 5% of its citizens were Sikhs. Of the rest, about two-thirds were Muslims and one-third Hindus. It is sad that Nehra’s good relationship with fellow Indians of a different religion was not widely reflected among the people of the sub-continent, when independence from Britain was achieved in 1947, and partition led to sectarian violence.
In a biographical article in “The Indian”, about ‘the editor’, Nehra described himself as ‘a man of very abstemious habits.’ He disliked smoking and drinking, and preferred lemonade to tea. Of his daily routine he wrote:
‘Even though he has been away from India for so many years, yet he is an early riser and starts work at six and never misses his morning bath. He takes pleasure in his work and that is why he works for 14 hours and sleeps for 8 and the rest of the time he employs in attending to daily needs and a little relaxation between the hours of 8 and 9 in the evening.’
He believed in devoting 10% of his profits and 5% of his time to charitable work and institutions. His hobbies were ‘building, books, journalism and social gatherings’, and his sporting interests were ‘swimming, tennis and driving.’ Both Mr and Mrs Nehra were keen tennis players (perhaps that is how they met, in Mombasa), and as the “Metroland” homes in Chalkhill Road were built on large plots, some would have had a tennis court in their back garden.
Aerial view of the Chalkhill and Barn Hill estates,
March 1939, with “The Shalimar” arrowed.
(Source: Brent Archives)
Although Nehra claimed in his biographical note that ‘by temperament he is always cheerful and hospitable’, and that he did not ‘indulge in anger or fiery outbursts’, he was not afraid to express his views quite forcefully. One regular feature of “The Indian” was his “Open Letters for the Public Good”, and he wrote them ‘without fear, favour or malice’.
Being free to speak truth to power is an important part of any good democracy. One of his letters was to the newly appointed Secretary of State for the Colonies, in Stanley Baldwin’s National Government of June 1935. After giving ‘hearty congratulations on your appointment’, he encouraged the Minister to ‘follow the spirit expressed by His Royal Majesty the King in his memorable Jubilee message’, and respect the rights of all people of different classes, colour, creed and countries. He went on:
‘You know, Indians form a larger majority of immigrants in the Colonies than any other race. Owing to the peace-loving disposition of Indians, their legitimate rights and interests have so far not been well protected in any of the Colonies. The local white immigrants out of sheer short-sightedness and selfishness are ill-treating the British Indians in nearly all the Colonies. The local Governors often yield to the local influence of the white agitation and pressure. It is for you to keep the balance and assist or direct, as the case may be, the local governors to treat Indians justly and fairly. Remember that the interests of the Empire and world peace are more important and vital than the interests of a handful of Englishmen or Europeans in a Colony.’
Nehra was well aware of the injustices which could occur in the Colonies, because he was a Privy Council agent. That meant he could act as a legal representative, on behalf of people or companies appealing to the Judicial Committee of the Privy Council in London. This acted as the Court of Appeal for cases decided in High Courts across the British Empire.
“The Indian” included a section devoted to reports of Privy Council hearings. One interesting case was an appeal by a lawyer and a newspaper editor, seeking to overturn a judgement against them by the Allahabad High Court for contempt of court. Their “contempt” was publicly alleging that inferior judges had been appointed to the Allahabad High Court, and that better qualified candidates had been overlooked, because of their caste.
R. Nehra & Co are shown as the agent in a number of cases. In one, Nehra represented the respondent in an appeal by the Bombay Commissioner of Income Tax, against a judgement of the High Court in Bombay (Mumbai), where the point at issue was ‘whether the rights of a woman under a family settlement have been forfeited owing to unchastity.’
Through his magazine, Nehra published the results of all Indian students who had come to England to study law, as well as giving the overall results for Bar exams. One example from 1935 was: ‘Examined, 223; Passed,154 (Indians, 44)’. He also gave advice to Indians coming to here to study:
‘Do not buy or bring many suits with you from India, because they will not be used in England owing to their inferior cut and poor material. One or two pairs of shoes would be sufficient until your arrival in England. If possible, wait until you arrive here before you purchase your overcoat.’
As “The Indian” had a wide circulation among not just the worldwide Indian community, but also people in Britain with an interest in the sub-continent, it often carried “small ads”. Here are just a couple of typical examples:
INDIAN LADY medical student requires board lodging with a private family, 2 years’ course or more. Give full particulars. — Box 454, c/o The Indian.
CEYLON STUDENT wants boarding house near a tennis club. — Write Box 458, c/o The Indian.
Nehra welcomed new Indian students to London with a reception at Veeraswamy’s in Regent Street. This was the capital’s first Indian restaurant, and had introduced Indian food to this country in the Indian Pavilion at the British Empire Exhibition, held at Wembley in 1924/25.
Veeraswamy’s Restaurant, in a BEE advertisement and at Regent Street. (Images from the internet)
This was Nehra’s advice on food to Indians coming here:
‘You may find some difficulty regarding food. There are many Indian Restaurants and Hostels that cater for Indians. At the beginning it will be of great help if you make use of these establishments, till you slowly get thoroughly accustomed to the western tasteless foods.’
As well as all of his other interests, Ram Singh Nehra still had political ambitions. This paragraph appeared in a newspaper in April 1936:
(Image from the internet)
Did Nehra stand for election to Parliament,
and what other twists and turns did his life take in the late 1930s? Please
join me next weekend, for the concluding part of his story.
Philip Grant,
December 2021.